What is Pitocin?
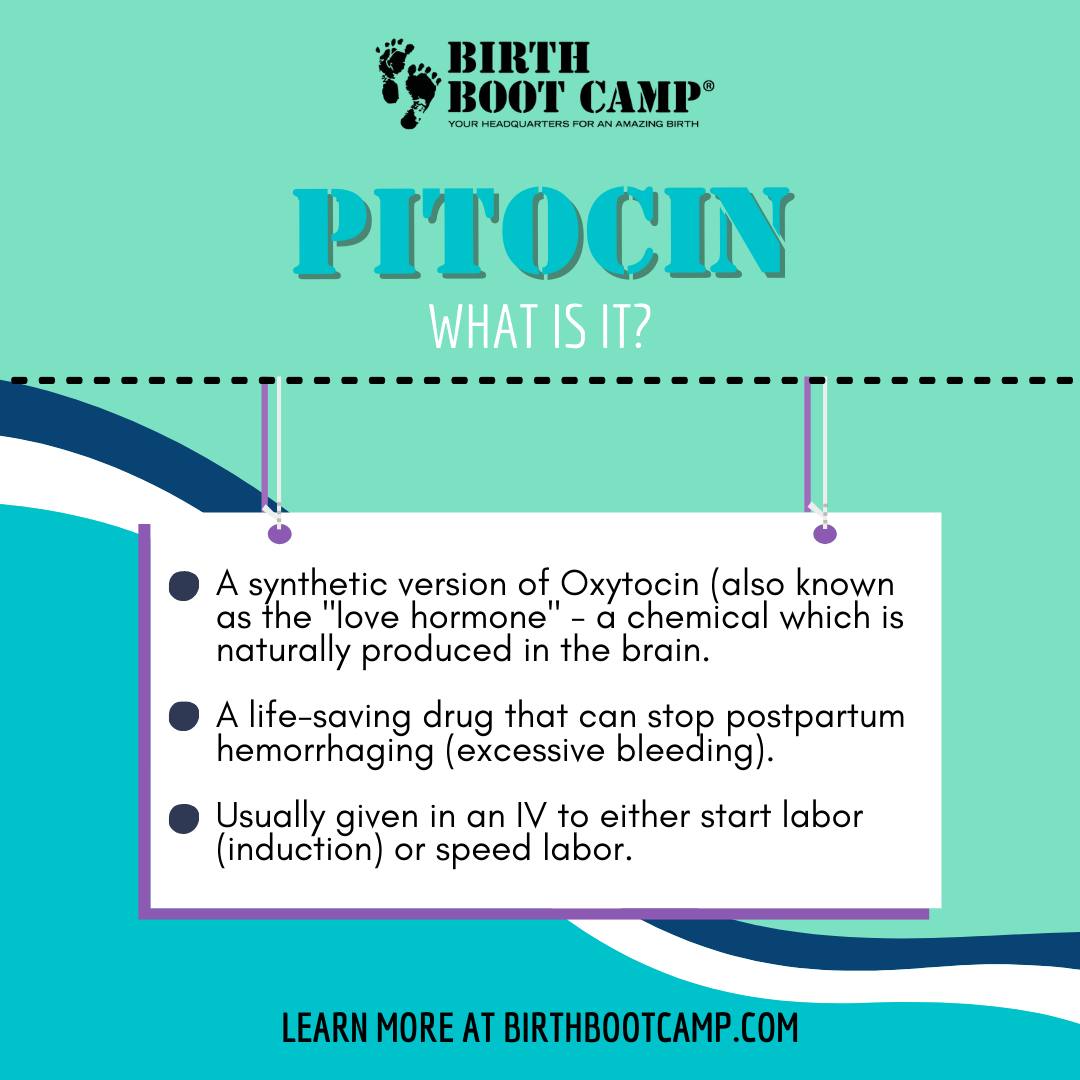
First synthesized around 1953, Pitocin is now commonly used in labor and delivery both to begin or speed labor. It can also be used postpartum to stop excessive bleeding or hemorrhage, which can be life threatening if left untreated.
While Pitocin is chemically the same as your body’s naturally produced oxytocin, there are some important differences between the two. The naturally occurring hormone oxytocin is produced in the pituitary gland of the human brain. Also called the “love hormone”, oxytocin is particularly important in the mechanism of birth (causing uterine contractions during labor and post labor) and in the milk letdown reflex during breastfeeding. Contractions caused by your bodies own oxytocin have a rhythmic pattern, like waves on the ocean and don’t normally last longer than a minute or a minute and a half. Oxytocin also has an emotional impact causing feelings of bonding, attachment and love.
Pitocin works slightly differently.Because Pitocin the drug is destroyed in your gut, it is often administered via an IV (intravenous line) during or after labor. Pitocin also has a relatively short half life in your blood (three minutes) so it must be continuously administered. This continuous administration can cause longer contractions than would normally be produced by a woman’s body alone.
Oxytocin is produced in the brain, but Pitocin does not cross the blood-brain barrier. Pitocin causes physical results similar to oxytocin (contractions) but lacks the power to cause emotional feelings of love and attachment like natural oxytocin does.
Pitocin administered to stop postpartum bleeding can be added to an IV or can be given via an intramuscular shot, typically after the delivery of the placenta.
Side effects of Pitocin
Pitocin has benefits and risks. Probably the most commonly talked about side effect of Pitocin is intense or painful contractions, though other side effects like vomiting or memory loss are mentioned in the literature. More serious side effects of Pitocin can occur. Misuse of Pitocin can cause fluid retention, uterine rupture, painful contractions, and hyperstimulation, which puts both the baby and the mother at risk.
Hyperstimulation is when contractions become extremely intense and come in much shorter timeframes. This can cause intense pain for the mother and puts her at risk of uterine rupture, postpartum hemorrhage, and lacerations on the cervix or vagina.
Pitocin and labor induction
The package insert for Pitocin says that, “Since the available data are inadequate to evaluate the benefits-to-risks considerations, Pitocin is not indicated for elective induction of labor.” Elective induction is an induction for no medical reason.
It is also interesting to note that induction (which is commonly accomplished using Pitocin) has a dramatic impact on the chances of cesarean section, particularly among first time mothers. In a study of 7,800 first-time mothers who gave birth at one U.S. medical center, researchers found that those who had their labor induced were about twice as likely to ultimately need a C-section.
A trusted care provider can help ensure that this lifesaving but potentially harmful drug is used appropriately for you and your birth and your baby.

*Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.